Agronomy
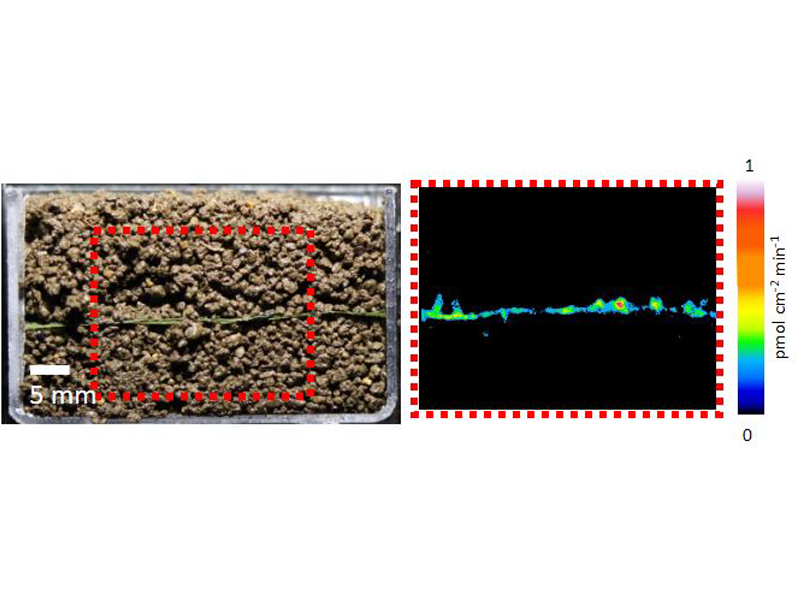
Earth’s carbon cycle works on a global scale. But it can be affected by the tiniest of organisms: soil microbes. These microbes decompose organic matter like plant litter and dead organisms, and create simple carbon compounds. These simple carbon compounds can then be used by other organisms, or turned into gases (like carbon dioxide) and released into the atmosphere.

If you’re a gardener, you know that planting seeds in the ground doesn’t always mean you’ll have a good yield at the end of growing season. On a personal level, this can be disappointing. Farmers are in charge of growing dozens to thousands of acres of food. And, they face the same variability in the planting, growing, and harvesting processes as gardeners do.

On average, Americans eat more than 50 pounds of beef each year (according to USDA estimates). But what do beef cattle eat? In the eastern United States, beef cattle often eat tall fescue, a “cool-season” grass. As the name suggests, cool-season grass grows best in temperate conditions: temperatures between 65 and 75 degrees Fahrenheit and abundant rainfall. But it’s not always cool and wet in the eastern U.S., and come the summer months, cool-season grasses tend to not do well.
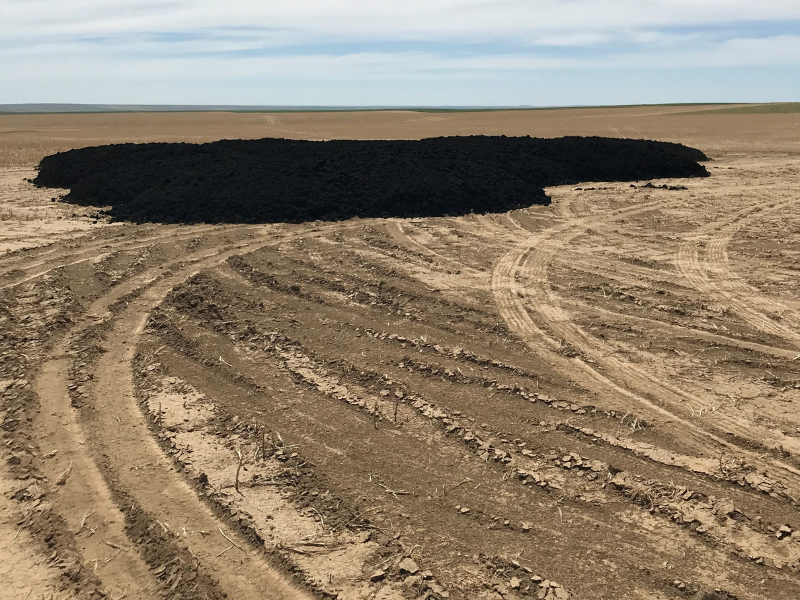

For more than four decades, biosolids have been applied to land and studied by researchers for many useful purposes. Biosolids are a product of the wastewater treatment process. Yes, that means sewage. However, the sewage is treated carefully to ensure it has beneficial properties and is not harmful.

Did you know one of the oldest life forms on Earth can be found in your backyard? Soil nematodes have been thriving in habitats around the world for at least 400 million years. Even though they are only 1/500th of an inch wide and 1/20th of an inch long, these worm-like animals are an important part in almost every ecosystem.

Winter grazing is part of what is called an integrated crop-livestock system. It is a process where livestock, such as cattle or goats, are allowed to graze a crop field during the winter. It is more common in climates with mild winters. Rather than eating the cash crop the farmer sells, the livestock eat the cover crop that was planted to grow over the winter.

Fields of amber grain may be the poetic image of American farmland. And it’s true that the U.S. grows plenty of wheat. But fields of yellow grain – corn – may be more accurate.




